Max Kopp Selected for 2025 Philly Inno’s 25 Under 25, Honored
The Business Journal and PHL Inno annually recognize promising young entrepreneurs and innovators in the region for the Inno Under 25 awards. This year, the program’s fifth, we’re recognizing 10 impressive individuals 25 years old or younger for their accomplishments.
The honorees span an array of industries, from health care to accelerators to media and content creation. Our 2025 class includes high school and college students as well as recent graduates, each looking to drive innovation and advancement with their nascent ventures.
Max is the founder and CEO of VitaSense, a research venture dedicated to building smart, lightweight sensing platforms for non-invasive glucose monitoring and spacecraft safety. At just 17, he has already earned multiple science awards, holds two U.S. patents pending, and is preparing a non-provisional patent for his most recent innovation: an ink-printed structural sensor system designed for deep space missions.
Maximilian Kopp – founder and CEO, Vitasense (Philadelphia)announcing the 2025 PHL Inno Under 25 honorees
Max kopp
AI-Powered Sensors for Healthcare

Max Kopp – Innovator in Wearable Healthcare & Nanotechnology
From an early age, Max Kopp exhibited a unique ability to merge scientific research, entrepreneurship, and leadership. His groundbreaking work in nanomaterials, biosensors, and wearable healthcare technology has led to award-winning innovations, high-impact publications, and global recognition. Focused on non-invasive glucose monitoring, polarized light optical sensing, and advanced biomedical engineering, Max is dedicated to bridging the gap between emerging technologies and real-world healthcare applications. Through his research, he strives to revolutionize medical diagnostics and wearable health solutions, making cutting-edge healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Max Kopp presenting Vitasense wearable device.
“AI-Powered Wearable Sensors for Healthcare”
“Revolutionizing Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring”
“Advancements in Nanomaterial-Based Sensors”
About Max Kopp
Max Kopp is an award-winning scientist, engineer, and entrepreneur revolutionizing wearable healthcare technology, non-invasive glucose monitoring, and nanomaterial-based sensors. With a strong foundation in chemistry, physics, and structural engineering, Max is leading advancements in polarized light optical sensing, biomedical sensor technology, and robotics-driven healthcare solutions.
As the driving force behind cutting-edge medical diagnostics and sensor technology, Max’s mission is to bridge the gap between scientific research and real-world applications, developing innovations that make healthcare more efficient, accessible, and non-invasive.
Max has conducted groundbreaking research in advanced materials and biomedical sensors, earning numerous awards and recognition for his contributions. His work focuses on developing next-generation technologies that integrate nanomaterials, optical sensing, and robotics to revolutionize wearable healthcare and structural diagnostics.
“Biomedical Engineering & Materials Science Expertise”
“Shaping the Future of Diabetes Care and Healthcare Innovation”


Max Kopp Research & Projects
1. Wearable Healthcare Technology
Max specializes in next-generation wearable biosensors, focusing on non-invasive glucose monitoring for individuals with diabetes. His nanomaterial-based sensors use polarized light optical sensing, paving the way for real-time health monitoring and smart medical devices.Biomedial Engineering: Polarized Light and Nanomaterials for Wearable Sensors
2. Nanomaterials & Biomedical Sensors
With expertise in nanomaterial applications, Max develops highly sensitive and flexible biosensors capable of detecting biomarkers for diseases, enhancing early diagnosis and patient care. His work integrates chemistry, materials science, and AI-powered healthcare analytics.
3.Structural Engineering & Aerospace Applications
Max’s research extends beyond wearable technology into structural diagnostics, using advanced sensors to detect material defects in aerospace and infrastructure. His innovations contribute to safer, more reliable engineering solutions for high-performance applications.Aerospace Science: Printable Sensors for Structural Defect Detection for Spacecraft and Deep-space Missions
4. Nonprofit Outreach_Kopp Foundation
Max Kopp is committed to raise Diabetes Awareness & Support, providing education, and supporting research for diabetes prevention and management. Empower individuals living with diabetes through mentorship, advocacy, and access to resources that improve their quality of life.

Official Registration of Kopp Foundation: This document from the Pennsylvania Department of State confirms the registration of the Kopp Foundation as a Domestic Nonprofit Corporation, with entity number 0014166124
5. President Volunteer Service Award by Whitehouse Recognition
Received national recognition from AmeriCorps and the White House.Recognized by President Joe Biden for global healthcare impacts



Max’s Achievements
With a strong background in physics, chemistry and engineering, Max has participated in numerous national and international science fairs, earning accolades for his innovative research.
Bronze Medalist in the S.-T. Yau High School Science Award (North America Division, 2024) for his project analyzing the polarized photoresponse of GeSe and its application in non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. This competition is one of the most rigorous high school science awards, attracting top young researchers worldwide.



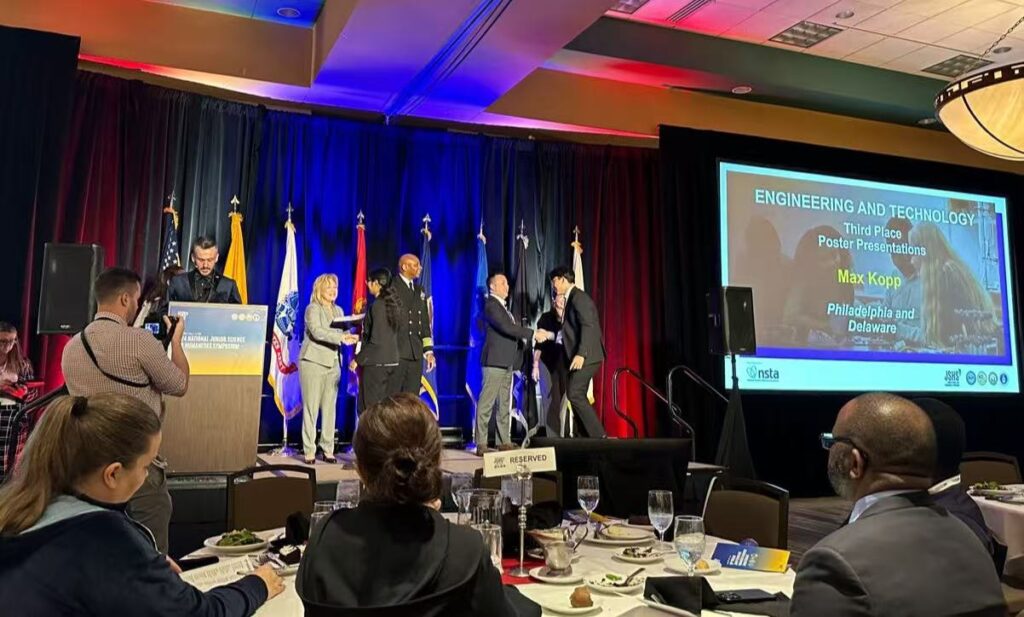
3rd Place in Engineering at the National Junior Science and Humanities Symposium (JSHS, 2024) for his research on flexible nanomaterial sensors. JSHS is an elite research competition with thousands of applicants, where only the best projects in STEM fields qualify for the national level.


Recipient of NASA recognition for his research contributions, demonstrating scientific excellence and innovation in materials science.
Material Science Research Award By W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.Issued by 2024 Delaware Valley Science Fair · Apr 2024. W. L. Gore & Associates is a global materials science company dedicated to transforming industries and improving lives.
Constellation Energy Engineering Award Issued by 2024 Montgomery County Science Research Competition,Mar 2024.Constellation (NASDAQ: CEG), the nation’s largest producer of carbon-free energy and a leading supplier of energy products and services, awarded $513,000 in E2 Energy to Educate grants for hands-on student projects.

Max’s Publication
Max Kopp has authored and published research papers on nanomaterials, sensor technology, and their applications. His notable work includes:
Analysis of the Polarized Photoresponse of GeSe and Its Application in Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring, which earned him a Bronze Medal at the S.-T. Yau High School Science Award (North America Division, 2024)
EWA:Flexible nanomaterial sensors for non-invasive health monitoring
Max is conducting a groundbreaking project focused on the development of ink-printed flexible sensors for structural defect detection. The project aims to enhance sensor durability, improve ink formulations, and achieve high sensitivity in extreme environments.Research Gate: Flexible nanomaterial sensors for non-invasive health monitoring
Inkjet-Printed Piezoelectric Nanomaterial Arrays for Autonomous Structural Health Monitoring in Spacecraft and Deep-Space Exploration.
This study presents an innovative, deployable inkjet-printed sensor array designed for real-time defect detection in spacecraft. The research focuses on leveraging piezoelectric nanomaterials for in-situ sensor fabrication, achieving sub-1% defect localization error and outperforming commercial ultrasonic sensors by 38% in sensitivity. The technology aims to enhance safety in long-duration space missions by enabling astronauts to fabricate and deploy sensors in microgravity environments.
Max KOPP:
Revolutionizing Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring

USPTO Patent Holder – Max Kopp was awarded a U.S. patent Pending for his non-invasive glucose monitoring technology. This innovation utilizes polarized light and nanomaterials to enable accurate, needle-free blood glucose measurement, offering a promising advancement for diabetes management.
Max’s Education
Max is Junior student of high school at Germantown Academy, he also has participated in prestigious educational programs such as:
- Harvard Summer School (General Chemistry) – Focused on nanomaterials for biomedical engineering, particularly their role in wearable sensor technology and drug delivery systems.
- Stanford Pre-College Program (Psychology) – Researched human cognition and the impact of wearable tech on health behaviors.
- Johns Hopkins University Center for Talented Youth (Advanced Computational Science) – Studied AI applications in biomedical engineering, focusing on data modeling and predictive analytics for healthcare solutions.


MAX KOPP: Entrepreneurial Venture
VitaSense:
Advancements in Nanomaterial-Based Sensors
Max Kopp is the founder of VitaSense, a startup focused on developing next-generation wearable sensors for non-invasive health monitoring. Built upon his award-winning research in nanomaterials and sensor technology, VitaSense aims to commercialize advanced biosensing solutions that improve real-time health tracking for individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes. The company integrates cutting-edge materials science with AI-driven analytics to create accurate, cost-effective, and user-friendly health monitoring devices. Max is currently leading research, prototyping, and business development efforts to bring VitaSense technology to market.
Vitasense – Award-Winning Innovation at the Conrad Challenge & Diamond Challenge
Revolutionizing Wearable Healthcare with Vitasense
Vitasense is an award-winning innovation in non-invasive glucose monitoring and wearable healthcare technology, developed by Max Kopp. The project has gained international recognition at the Conrad Challenge and the Diamond Challenge, two of the world’s most prestigious entrepreneurship and science competitions. By combining nanomaterials, biomedical engineering, and optical sensing technology, Vitasense aims to transform diabetes care and real-time health monitoring.
Vitasense at the Conrad Challenge – Innovating for Global Impact
The Conrad Challenge is a globally recognized competition that fosters scientific innovation and entrepreneurship. Vitasense stood out in this competition for its groundbreaking approach to wearable healthcare technology, utilizing polarized light optical sensing and nanomaterial-based sensors to create a non-invasive glucose monitoring solution.
🏆 Key Achievements at Conrad Challenge:
- Developed a revolutionary biosensor technology that enables continuous, non-invasive glucose tracking.
- Recognized for its potential to revolutionize diabetes management, making health monitoring more accessible and user-friendly.
- Integrated AI-powered diagnostics to enhance accuracy and efficiency in biomedical sensing.
Through the Conrad Challenge, Vitasense was recognized as a game-changing technology in healthcare, highlighting Max Kopp’s expertise in nanotechnology, physics, and biomedical engineering.
Vitasense at the Diamond Challenge – Business & Market Viability
The Diamond Challenge, organized by the University of Delaware, is one of the most competitive high school entrepreneurship competitions, providing young innovators with a platform to develop scalable business solutions.
In the Diamond Challenge, Vitasense was celebrated for its strong commercial potential and disruptive impact in wearable healthcare. By bridging science and entrepreneurship, Max Kopp developed a market-ready solution that addresses a growing demand for non-invasive glucose monitoring.
🏆 Key Achievements at Diamond Challenge:
- Designed a scalable business model for a wearable healthcare startup.
- Demonstrated strong market validation, showing high demand for non-invasive health monitoring solutions.
- Showcased leadership, strategy, and business development skills in a globally recognized competition.
Through the Diamond Challenge, Vitasense was established as a high-impact startup concept, paving the way for future commercialization and industry partnerships.
The Future of Vitasense – Bridging Science & Entrepreneurship
With its success at the Conrad Challenge and Diamond Challenge, Vitasense is positioned to become a leading innovation in wearable biosensors and non-invasive healthcare technology. By integrating advanced nanomaterials, AI-driven diagnostics, and biomedical engineering, Max Kopp is spearheading a new era of real-time, user-friendly health monitoring solutions.













